소프트웨어(SW) 통계포털은 SW생산, SW수출, SW인력, 신SW산업 분야 등 소프트웨어와 관련된 다양한 통계를 제공하고 있습니다.
- RE-092
국가연구개발사업에서의 SW융합 현황 분석에 관한 연구
- 서영희 역대연구원
날짜2020.04.21
조회수15596
-
- 1. 제 목 : 국가연구개발사업의 SW 융합 현황 분석에 관한 연구
- 2. 연구 목적 및 필요성
- (1) 추진 배경
- 제4차 산업혁명의 핵심 동인은 소프트웨어(이하 SW)로써 전 산업의 생산성과 글로벌 경쟁력을 제고하고 사회 문제를 해결하여 혁신 성장을 주도하고 있음
- 글로벌 시장은 이미 SW 기업을 중심으로 재편중이며 SW가 핵심 역량으로 부각하고 있기 때문에 지능화 혁신의 주체로써 인공지능, 빅데이터, 클라우드 등 SW 신기술의 고도화 및 전 산업의 디지털 전환을 위해 기존의 SW 산업을 위한 R&D 정책에서 벗어나 현황에 맞는 정부 차원의 R&D 정책에 대한 전략 수립이 필요함
- SW 중요성의 제고로 부처별로 국가연구개발사업을 통해 SW 융합 과제를 진행하고 있으며 정성적 방법론을 활용한 SW 융합 R&D 조사가 이루어졌으나 방대한 시간과 비용이 투입되며 지속적인 분석에 어려움이 존재함
- →SW 융합 역량 제고를 위한 SW 융합 현상에 대한 부처별, 분야별 등의 유형별 통계 자료가 필요하나 현재까지는 정량적 방법을 활용하여 자동으로 SW 융합 R&D 단계를 분류하는 방법이 제시되고 있지 못한다는 것이 본 연구의 출발점임
- (2) 연구의 목적
- 본 연구는 국가연구개발사업의 과제 중 SW 융합 R&D 과제를 자동으로 분류하기 위한 모델을 개발하여 SW 융합 R&D 현황을 조사하고 분석하여 SW 융합 역량 확보를 위한 SW 융합 R&D 정책 방향을 제시하는 것임
- - 2018년에 수립된 판단 기준에 따라 전문가 델파이 조사의 결과 값을 입력 데이터로 활용하여 기계학습을 활용한 자동 분류 모델을 개발하고 2017년 연구개발과제에 대한 유형별 SW 융합 R&D 관련한 기초 자료를 확보하고자 함
- 3. 연구의 구성 및 방법
- (1) 연구의 구성
- 본 연구의 구성 및 진행 방법은 아래와 같이 총 5단계로 구성됨
- [그림 1] 연구 진행 단계
![[그림 1] 연구 진행 단계](/webroot/lib/fileman/Uploads/post_images/2020_03/RE_092_1.png)
- ① (1단계) 정량적으로 SW 융합 R&D 현황을 분석하기 위해 기존에 수행된 연구에 대한 정리 및 SW 융합 R&D 기준에 대해 알아보고, 국외 SW 융합 R&D 정책에 대한 현황을 정리함
② (2단계) SW 융합 R&D의 자동 분류를 위한 기계학습 모델을 개발하기 위해 학습 데이터인 국가연구개발과제의 연구 요약문 관련 텍스트에 대한 전처리 과정을 거쳐 세 가지의 기계학습 모델에 대한 실험을 통해 모델을 선택함
③ (3단계) 선택된 분류 모델을 활용하여 2017년 국가연구개발과제를 대상으로 총 3가지(2/3/5단계) 형태로 SW 융합 R&D에 대한 예측 및 예측 결과에 대한 신뢰도 검증 수행
④ (4단계) 2017년 국가연구개발과제의 예측 결과를 토대로 수행 부처, 국가표준분류체계(대분류), 수행 주체, 연구개발 단계라는 총 4가지의 유형별 SW 융합 R&D 현황 분석을 위해 시각화 도구를 활용하여 분석을 수행함
⑤ (5단계) 3단계의 SW 융합 R&D 현황을 토대로 향후 SW 융합 활성화를 위한 정책적 시사점 및 발전 방향을 도출함 - (2) 연구의 방법
- SW 융합 R&D 과제에 대한 자동 분류 모델 개발을 위해 선행 연구 분석 및 다양한 분류 모델에 대한 실험 및 검증을 거쳐 SW 융합 R&D 전문가 자문 회의 등을 통해 SW 융합 R&D 현황 분석 및 시사점을 도출함
- ① 텍스트 마이닝 방법
- 중요 단어의 추출 시에 대표적으로 활용되며 텍스트 내에 특정 단어의 상대적 중요도를 계산하는 통계적인 수치인 tf-idf 방법과 문서를 벡터로 표현하는 방법론인 doc2vec을 활용하여 각 결과 값을 비교·분석함
② 기계학습 모델 선택
- 로지스틱 회귀(Logistic Regression)와 Support Vector Machine(SVM), 다항 나이브 베이즈(Multinomial Naive Bayes)를 비교·분석하여 최상의 모델을 선택함 -
기계학습 모델 - 기계학습 모델, 설명 순서로 구성된 표 기계학습 모델 설명 로지스틱 회귀 종속 변수가 0이나 1인 이진형 변수에서 자주 사용하는 분류 방식 Support Vector
Machine(SVM)입력 공간과 관련된 비선형 문제를 고차원 공간의 선형문제로 사상(projection)시켜 나타냄 다항 나이브 베이즈 신뢰도가 높고 효율적인 문서 분류기로 널리 사용되는 기분 문서 분류 방법 - 4. 연구 내용 및 결과
- (1) SW 융합 R&D 분류 모델 예측 결과 및 단계 소개
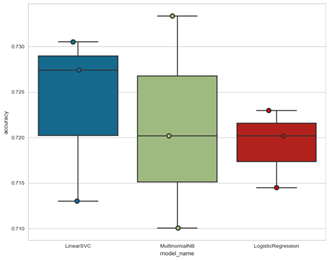
- SW 융합 R&D 단계의 구분을 위해 2가지의 텍스트 마이닝 기법과 3가지의 모델을 실험을 수행하였으며, 모델의 성능은 정확도(Accuracy)와 정밀도(Precision), 재현율(Recall)을 활용하여 측정하고 결과를 비교함
- - 정확도는 입력 단계를 그대로 정확히 맞추어야 정답으로 인정하는 정 매칭과 중간 3개 단계를 결합하여 하나의 단계로 간주하는 결합 매칭, 실제 결과와 1단계 떨어진 예측 결과를 보이면 맞은 것으로 간주하는 인접 매칭으로 나누어 실험을 진행함
- [그림 2] 모델별 정확도 실험 결과
![[그림 2] 모델별 정확도 실험 결과](/webroot/lib/fileman/Uploads/post_images/2020_03/RE_092_2.png)
- (2) 텍스트 마이닝 결과
- 본 연구에서 활용한 텍스트 형태의 입력 자료에 대한 벡터화 결과는 <표 1>과 같이 doc2vec 보다 tf-idf가 평균적으로 예측력이 높은 것으로 나타남
- - doc2vec 알고리즘은 일반적으로 학습 데이터가 많은 경우에 보다 더 좋은 성능을 보이기 때문에 학습 데이터가 상대적으로 적은 현 실험에서는 tf-idf가 상대적으로 더 바람직한 알고리즘으로 판단됨
- doc2vec은 실험을 수행하는 과정에서 입력 단어에 대한 추론(inference)으로 인해 입력 데이터 전체를 벡터화하기 위해 요구되는 시간이 tf-idf에 비해 현저하게 많이 필요하다는 단점이 존재함 - [표 2]tf-idf/doc2vec의 학습 결과 비교(5단계 & Linear SVM 기준)
[표 2]tf-idf/doc2vec의 학습 결과 비교(5단계 & Linear SVM 기준) - 구분, 단계, 정밀도, 재현율, f-score의 순서로 구성된 표 구분 단계
(Scale)정밀도
(Precision)재현율
(Recall)f1-
scoretf-idf High 0.59 0.76 0.67 Med High 0.17 0.06 0.09 Medium 0.18 0.07 0.09 Med Low 0.22 0.06 0.09 Low 0.83 0.95 0.89 정확도
(Accuracy)Accurate matches:72.78%
Combined matches:75.31%
Adjacent matches:84.50%doc2vec High 0.57 0.75 0.64 Med High 0.21 0.09 0.12 Medium 0.10 0.05 0.07 Med Low 0.07 0.01 0.03 Low 0.82 0.94 0.88 정확도
(Accuracy)Accurate matches:70.11%
Combined matches:73.19%
Adjacent matches:82.57% - (3) 2017년 국가연구개발과제의 예측 결과
- 1) Linear SVM 모델의 벡터화 알고리즘 및 단계별 예측 결과 비교
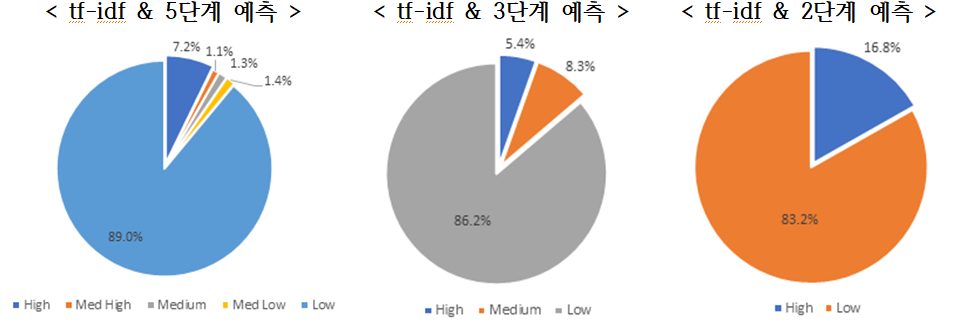
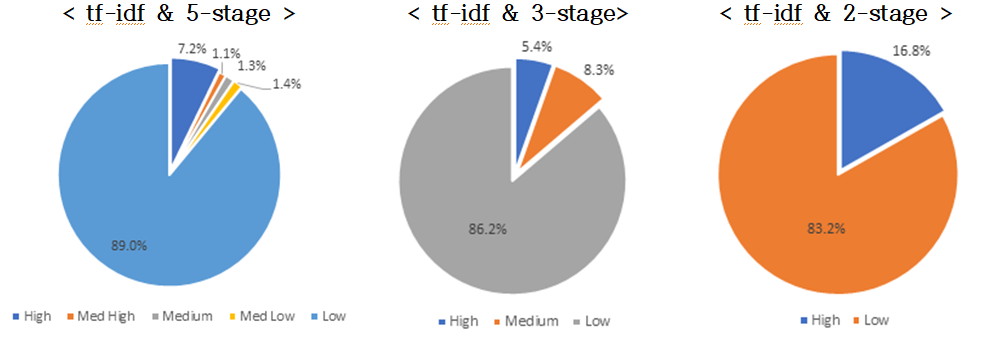
- Linear SVM 모델과 tf-idf/doc2vec 알고리즘에 대한 실험 결과, tf-idf 방식의 2단계 예측 값이 2016년 학습 데이터와 가장 유사한 결과를 도출1)하였음
- - tf-idf방식의 2단계 예측 값으로 살펴본 결과, SW 융합 R&D가 차지하는 비중은 전체의 16.8%인 것으로 판단
- doc2vec은 각 단계별 치우침 현상이 상대적으로 적게 발생하여 5단계와 2단계 사이의 Low 단계의 비율 차이가 2.75%인 비교적 안정적인 모델로 나타남(tf-idf는 5.76% 차이를 보임)
- [표 3] 2017년도 국가연구개발과제 분류 결과 요약 (Linear SVM)
[표 3] 2017년도 국가연구개발과제 분류 결과 요약 (Linear SVM) - 공백, 5단계, 3단계, 2단계의 순서로 구성된 표 5단계 3단계 2단계 tf-idf High 4,012 7.22% High 3,022 5.44% High 9,325 16.78% Med High 587 1.06% Medium 4,623 8.32% Low 46,241 83.22% Medium 746 1.34% Low 47,920 86.24% Med Low 776 1.40% Low 49,445 88.98% doc2vec High 3,499 6.30% High 3,005 5.41% High 8,107 14.28% Med High 668 1.20% Medium 4,463 8.03% Low 48,678 85.72% Medium 1,070 1.96% Low 48,098 86.56% Med Low 1,313 2.36% Low 49,017 88.21% - [그림 3] Linear SVM & tf-idf 방식의 단계별 예측 분포
- 2) Multinomial NB 모델의 벡터화 알고리즘 및 단계별 예측 결과 비교
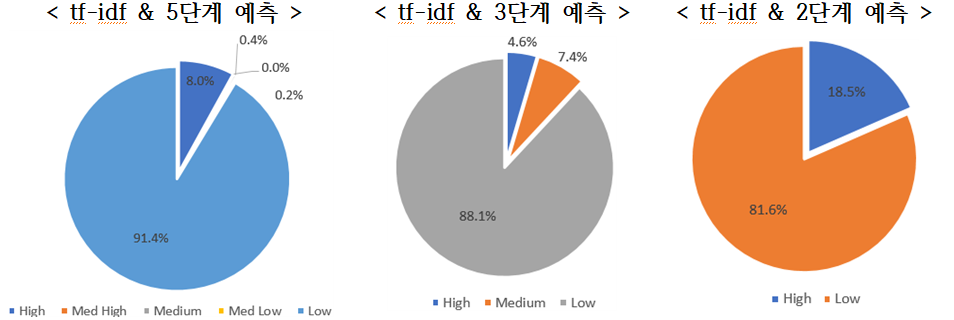
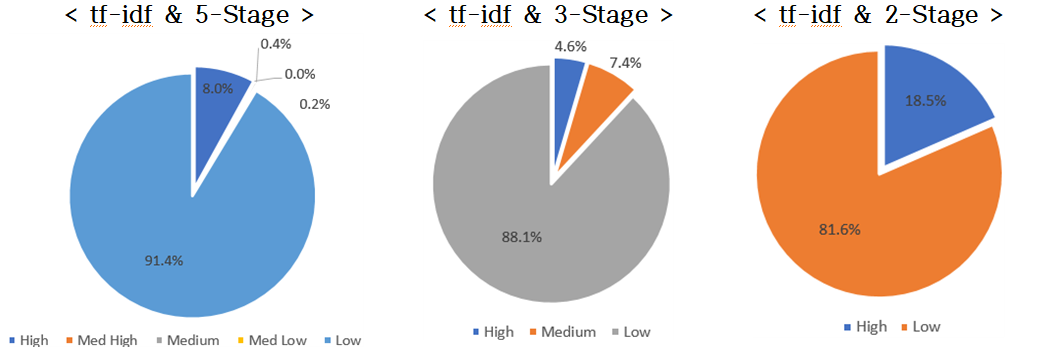
- 해당 모델은 <표 3>과 같이 5단계 예측에서 tf-idf와 doc2vec 모두 중간의 세 단계(Med High, Medium, Med Low)의 예측을 거의 하지 못하며, 특히 Med High 단계의 과제를 거의 분류하지 못한 것으로 나타났음
- 두 알고리즘에서 모두 5단계와 3단계 구분에서 Low 단계로 구분한 과제가 약 90% 초반과 약 88% 정도의 수치를 보이고 있어 2016년 학습 데이터에 비해 Low 단계로의 예측에 대한 쏠림 현상이 존재함
- - tf-idf의 결과에서 2단계와 5단계의 Low 단계에 대한 비율 차이는 9.87%이고, doc2vec은 10.75%의 차이를 보임
- [표 4] 2017년도 국가연구개발과제 분류 결과 요약(Multinomial NB)
[표 4] 2017년도 국가연구개발과제 분류 결과 요약(Multinomial NB) - 공백, 5단계, 3단계, 2단계의 순서로 구성된 표 5단계 3단계 2단계 tf-idf High 4,513 7.95% High 2,590 4.56% High 10,477 18.45% Med High 9 0.02% Medium 4,185 7.37% Low 46,308 81.55% Medium 241 0.42% Low 50,010 88.07% Med Low 109 0.19% Low 51,913 91.42% doc2vec High 3,736 6.58% High 2,534 4.46% High 10,129 17.84% Med High 0 0.00% Medium 3,976 7.00% Low 46,656 82.16% Medium 89 0.16% Low 50,275 88.54% Med Low 200 0.35% Low 52,760 92.91% - [그림 4] Multinomial NB & tf-idf 방식의 단계별 예측 분포
- (4) 예측에 대한 전문가 검증 결과
- 100건의 표본 추출 후, SW 융합 R&D 전문가의 검증을 수행하여 모델의 예측 결과와 비교한 결과, 종합적으로 자동 분류 모델이 예측한 결과는 SW R&D 전문가가 분류한 결과와 86%가 일치하는 것을 확인함
- - High 단계는 두 결과가 75%, Med High와 Medium 단계는 16.7%가 일치하며, 이는 학습 데이터가 가지는 특성 때문에 Med High, Medium과 Med Low 단계는 전문가와 분류 모델이 일치하는 결과가 적다고 판단할 수 있음
- 본 연구의 분류 모델이 중간(Med*) 단계에 해당하는 과제를 상대적으로 과소하게 예측하는 경향을 보이며 High와 Low 단계의 구분에 더 특화된 것을 알 수 있음
- [표 5] 전문가 예측 기준 정 매칭, 인접 매칭, 비 매칭 수와 비중
[표 5] 전문가 예측 기준 정 매칭, 인접 매칭, 비 매칭 수와 비중 - 전문가 예측, 개수, 정 매칭 개수와 비중, 인접 매칭의 개수와 비중, 비 매칭의 개수와 비중 순서로 구성된 표 전문가 예측 개수 정 매칭 인접 매칭 비 매칭 개수 비중 개수 비중 개수 비중 High 8 6 75.0% 0 0.0% 2 25.0% Med High 6 1 16.7% 1 16.7% 4 66.7% Medium 6 1 16.7% 0 0.0% 5 83.3% Med Low 2 0 0.0% 2 100.0% 0 0.0% Low 78 78 100.0% 0 0.0% 0 0.0% 합계 100 86 86.0% 3 3.0% 11 11.0% - (5) 모델 예측에 대한 설명
- 분류 모델의 활용도 및 신뢰도를 높이기 위해 분류의 근거가 되는 설명을 제공하고자 하며, Lime 알고리즘을 활용하여 과제의 분류 근거를 설명함
- - Lime은 입력 데이터를 변경시켜 가면서 예측이 어떻게 변하는지를 확인함으로써 특정 예에 대한 분류 모델의 결정에 대한 설명을 시도하는 블랙박스에 대한 설명자임
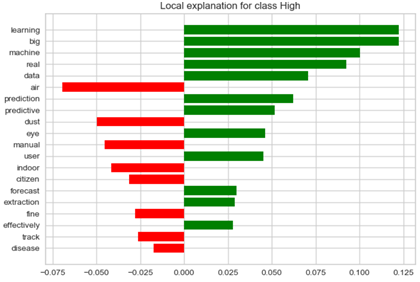
- [그림 3]은 High 단계로 분류된 데이터에 대한 분류 근거를 설명한 것으로 “learning”, “big”등이 긍정적 영향을 미치고, “air”, “dust”등이 부정적 영향을 미쳤으나 긍정의 기여도가 높아 High 단계가 결정됨 - [그림 5] High 단계 판단에 대한 각 단어의 가중치 그래프
- (6) SW 융합 R&D의 유형별 분석 및 시사점
- 자동 분류기를 활용하여 2017년 국가연구개발과제 중 예측 결과가 존재하는 총 55,566건의 예측 결과를 총 4가지(수행 부처, 수행 주체, 연구개발 단계, 과학기술표준분류체계)의 유형별로 현황을 분석하고자 함
- ① 수행 부처별
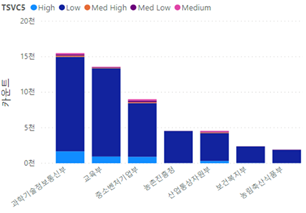
- [그림 6] 부처별 5단계 구분 결과(과제 수 기준, 상위 7개)
- [그림 7] 부처별 5단계 구분 결과(총 연구비 기준, 상위 7개)
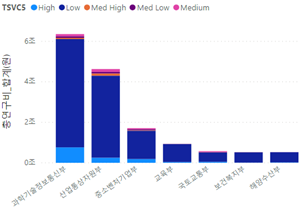
- (현황) 5단계 구분 및 총 연구비 기준으로 SW 융합 R&D를 가장 많이 수행한 주체는 과학기술정보통신부(이하 과기정통부), 산업통상자원부(이하 산업부), 중소벤처기업부(이하 중기부)로 나타났으며 과제 수 기준으로는 과기정통부, 교육부, 중기부 순으로 조사됨
- - (과기정통부) 과기정통부가 타 부처에 비해 SW 융합 R&D 활동을 80% 이상 포함하는 단계인 High 단계의 과제를 가장 많이 활발하게 수행하는 주체로 나타남
- High 단계에서 과제 수 기준으로 교육부(2번째)에 비해 약 1.8배 정도 많은 과제를 진행하였으며, 총 연구비 측면에서는 산업부(2번째)에 비해 약 3배 정도 큰 금액을 차지하고 있음
- - (중기부) 과제 수 기준으로 SW 융합 R&D 활동이 20~60% 정도(Medium, Med Low 단계)인 과제를 가장 많이 수행하는 부처로 나타났음
- (산업부) 총 연구비 기준으로 SW 융합 R&D 활동이 40~80% 사이(Med High, Medium 단계)의 과제를 가장 활발히 수행하는 부처로 조사되었음 - [그림 8] 부처별 연구비 및 SW 융합 과제 현황
- (시사점) SW 융합 R&D 과제는 국가연구개발사업*에 비해 상대적으로 부처별로 균형 있게 수행되지 않아 SW 융합 활성화를 위한 전략 마련이 필요
- - 총 연구비 기준으로 과기정통부, 산업부, 중기부가 차지하는 비중의 합이 82.58%이나 그 외 20개 부처는 합계가 10% 미만으로 매우 저조한 상황
국가연구개발사업 전체의 총 연구비에서 위 3개 부처가 차지하는 비중은 76.38%임
- 국가연구개발사업에서 SW 융합이 부처별로 균형 있게 이루어지지 않고 있다는 점에서 SW 융합 제고를 위한 부처별 SW 융합 R&D 기획* 및 범부처 차원의 SW 융합 과제의 연계 기획 및 지원 등의 정책 수립이 요구됨
보건복지부, 농림축산식품부 등의 각종 통계 처리 및 현황 분석이나 기상청의 기상 예측 모델 등에 SW를 융합한 R&D의 시범 적용 및 확대 등 - ② 수행 주체별
- [그림 9] 수행 주체별 연구비 및 SW 융합 과제 현황
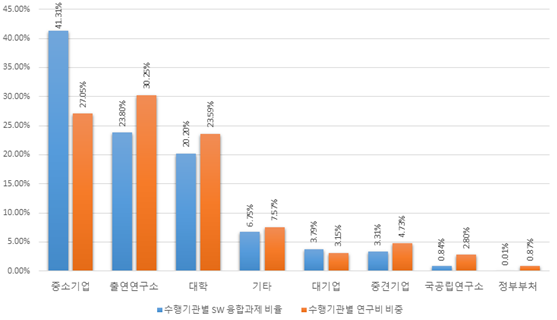
- (현황) SW 융합 과제를 주로 수행하는 주체는 중소기업, 출연연구소, 대학 순으로 나타나고 있으나 대기업, 중견기업, 국공립연구소 등은 SW 융합 과제에서 차지하는 비중이 5% 미만으로 매우 저조한 것으로 나타남
- - 중소기업은 총 연구비 기준에서 Low 단계를 제외한 모든 SW 융합 R&D 단계에서 과제를 가장 많이 수행하고 있는 주체로 나타났으며, 대학은 과제 수 기준으로는 High와 Med High 단계에서 SW 융합 R&D 과제를 가장 많이 수행하는 주체로 조사됨
- 출연연구소는 총 연구비 기준으로 전체 국가연구개발과제 중 30% 정도를 수행하고 있으나 이에 비해 SW 융합 R&D 과제를 적극적으로 수행하는 주체가 아닌 것으로 나타남 - [그림 10] 연구수행 주체-5가지 단계(과제 수)
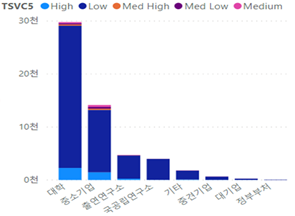
- [그림 11] 연구수행 주체-5가지 단계(연구비)
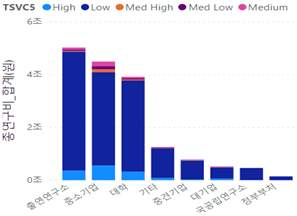
- (시사점) 국가연구개발과제에 대한 총 연구비 비중은 출연연구소, 대학, 중소기업 순이나 SW 융합 과제는 이의 역순으로 조사되어 출연연구소의 SW 융합 R&D 활성화를 위한 노력이 필요함
- - 국가연구개발과제의 30% 이상의 연구비를 사용하는 출연연구소의 SW 융합 R&D를 통한 경쟁력 확보 및 수행한 연구 성과가 SW 융합 과제의 핵심 주체인 중소기업을 통해 사업화로 연결되기 위한 제도적 지원이 요구됨
- ③ 연구개발 단계
- (현황) 국가연구개발과제의 총 연구비에 대한 단계별 비중은 개발, 기초, 응용연구 순으로 높게 나타났으며, SW 융합 R&D도 동일한 것으로 나타남
- - SW 융합 R&D는 개발연구가 국가연구개발에 비해 다소 높은 비중인 52% 이상을 차지하고 있으며, 이는 SW R&D의 특성과 일치하는 현상인 것으로 판단됨
- [그림 12] 연구단계별 연구비 및 SW 융합 과제 현황
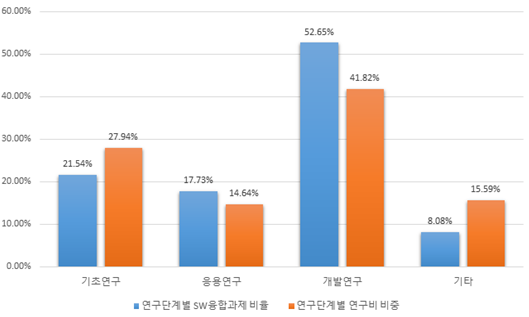
- (시사점) SW R&D는 기초 단계에 해당하는 새로운 사실의 발견보다는 제품·서비스의 창출을 목표로 하는 특성을 가지고 있기 때문에 개발 단계의 비중이 일반 연구개발보다 높은 것은 이를 반영한 현상인 것으로 판단됨
- ④ 국가과학기술표준분류체계의 대분류
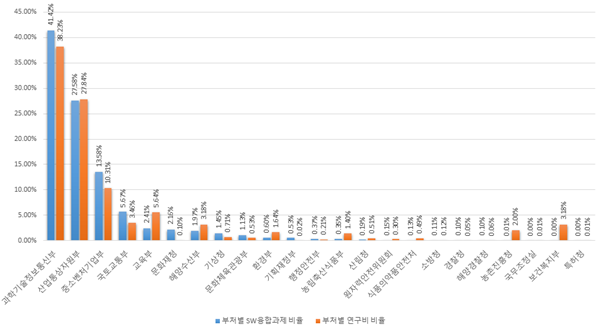
- (현황) 정보/통신과 전기/전자와 같은 일부 분야는 SW 융합 비율이 높으나 생명과학, 농업 관련 분야는 SW 융합 정도가 미흡한 것으로 조사되어 균형있는 SW 융합을 위한 정책 수립이 필요함
- - 정보/통신 분야는 국가연구개발사업에서 차지하는 비중(11.1%)에 비해 SW 융합 R&D 과제 전체의 연구비에서 차지하는 비중이 3배 이상(36.7%) 높게 나타났으며 국가연구개발사업과 가장 큰 차이를 보임
- 전기/전자와 건설/교통, 문화/예술/체육 분야 역시 국가연구개발사업에서 차지하는 분야별 비율에 비해 SW 융합 R&D 비율이 높은 것으로 나타나 SW 융합이 높은 것으로 조사됨
- 생명과학과 농림수산식품, 재료, 화공 등의 분야는 국가연구개발의 총 연구비에서 차지하는 분야의 비중에 비해 SW 융합 정도가 현저히 떨어지는 것으로 나타남 - [그림 13] 과학기술표준분류체계별 연구비 및 SW 융합 과제 현황
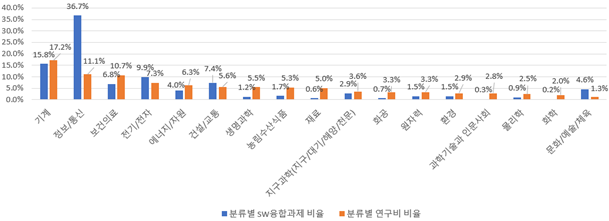
- (시사점) 분야별 SW 융합 정도의 차이가 존재하여 분야별 글로벌 경쟁력 강화를 위한 전략적 포트폴리오의 수립이 요구됨
- - 융합이 저조한 생명과학과 농림수산식품, 재료, 화공 등의 분야에서 SW 융합을 통한 효율성 제고 및 경쟁력 확보를 위해 SW 융합 R&D 과제의 기획 및 관련 성과에 대한 홍보 등의 전략 마련이 필요함
- 5. 정책적 활용 내용
- 본 연구의 결과물인 SW 융합 R&D 자동 분류 모델을 통해 국가 연구개발 사업 전체에 대한 SW 융합 현황에 대한 분석이 가능하며 기존의 전문가를 활용한 분석 방법에 비해 투입되는 자원과 시간을 절약하고 매년 데이터에 기반한 추이 분석을 할 수 있음
- - 이를 통해 구체적인 SW 융합 R&D 현황 및 근거 자료를 확보하여 향후 중장기 SW 융합 R&D 전략 및 정책 수립 시 기초 자료로 활용이 가능함
- 본 연구에서는 기존의 정성적 방법이 아닌 정량적인 방법으로 SW 융합 R&D 판단 기준을 수립하고, 2017년 NTIS에서 제공한 과제 정보를 기반으로 조사를 수행하여 현황 및 현안을 도출하고, 향후 SW 융합 R&D 활성화에 대한 정책적 개선 방향을 제시하였음
- 본 연구에서 수행한 국외 SW 관련 R&D 정책 분석과 국내 국가연구개발과제의 SW 융합 R&D 현황 분석을 통하여 SW 기술이 핵심 기반이 되고 있는 제4차 산업혁명 시대에 맞춰 전반적인 국가연구개발과제의 SW 융합 정도를 적절한 수준으로 향상하기 위한 정책 수립의 근거를 제시하였음 - 6. 기대 효과
- 국가연구개발사업 전반에서 일어나고 있는 SW 융합 현상을 지속적으로 파악하고 추이를 비교·분석할 수 있는 SW 융합 R&D 분석의 발판을 마련함
- - 인공지능 기술을 활용하여 기존의 많은 인력과 비용, 시간을 투입하여 표본 추출을 통해 전체의 과제를 추정하는 기존 연구의 제약점을 극복하여 매년 국가연구개발사업에 대한 연도별 SW 융합 확산 현상의 비교·분석을 빠르고 정확하게 수행할 수 있음
- 또한, NSF나 DARPA, EU의 Horizon 2020과 같은 국외 연구기관에서 수행되는 국가연구개발사업 관련 텍스트 데이터를 확보하여 자동 분류 모델을 적용할 수 있으며, 해당 결과를 국내 현황과 비교하는 추후 연구를 통해 시사점을 도출할 수 있음
-
SUMMARY
- 1. Title: Analysis of SW Convergence Status of National Research & Development Projects
- 2. Purpose and Necessity of the Research
- (1) Background of research
- The key driver of the fourth industrial revolution is software(SW), which enhances the productivity and global competitiveness of all industries and leads innovation growth by solving social problems.
- Global markets are already reorganizing around SW businesses. As SW is emerging as a key capability, it is necessary to establish a strategy for government-level R&D policies that are tailored to the current situation, moving away from the existing R&D policies for SW industries to develop and upgrade SW technologies such as artificial intelligence, big data and cloud as the main players for intelligent innovation.
- Because importance of SW is increasing, each ministry is carrying out task of convergence of SW through national R&D projects. In addition, although SW convergence R&D survey was conducted using qualitative methodology, it takes a lot of time and money and there are difficulties in continuous analysis
→ Statistical data for SW convergence phenomena are required by type, such as departmental and sector, to enhance SW convergence capabilities, but methods for automatically classifying SW convergence R&D steps have not been presented so far using quantitative methods. This study began to overcome this point - (2) Purpose of research
- This research is to develop a model for automatically classifying SW convergence R&D tasks among national R&D projects to investigate and analyze SW convergence R&D status to present SW convergence R&D policy direction for securing SW convergence capabilities.
- - Based on the criteria established in 2018, the results of the expert Delphi survey will be used as input data to develop an automatic classification model using machine learning and to secure basic data related to SW convergence R&D by type for the 2017 R&D project.
- 3. Composition and method of research
- (1) Composition of research
- The method of composition and progress of this study consists of a total of five stages.
- ① (Stage 1) To analyze the current status of SW convergence R&D in quantity, the existing research performed is organized and the SW convergence R&D criteria are explored, and the status of SW convergence R&D policies are summarized.
② (Stage 2) To develop a machine learning model for automatic classification of SW convergence R&D, the model is selected through experimentation on three machine learning models after preprocessing of the text related to the research summary of the national R&D task, which is learning data.
③ (Stage 3) Using the selected classification model, the national R&D project is carried out in 2/3/5 stages to verify the reliability of the prediction and results for SW convergence R&D.
④ (Stage 4) Based on the prediction results of the 2017 national R&D project, the analysis is carried out using visualization tools to analyze the current status of SW convergence R&D by type of department, national standard classification system, performance principal, and stage of execution.
⑤ (Stage 5) Based on the SW convergence R&D status of the three types of steps, policy implications and direction of development are derived for the activation of SW convergence in the future. - (2) Method of research
- To develop an automatic classification model for SW convergence R&D tasks, SW convergence R&D status analysis and implications are derived through SW convergence R&D expert consultation meetings, after prior research analysis and experimentation and verification of various classification models.
- ① Text mining method
- - Each result value is compared and analyzed using tf-idf method, which is a representative value used to extract important words, and a statistical value that calculates the relative importance of a specific word in the text, and doc2vec, which is a methodology for expressing a document as a vector.
- ② Select machine learning model
- - A total of three models are compared. Support Vector Machine (SVM), which refers to logistic regression, a type of classification frequently used in binary variables with a dependent variable of zero or one, and nonlinear problems associated with input space as linear problems in high-dimensional space, is the method of mood classification widely used as reliable and efficient document classification. Compare and analyze these models to finally select the best model.
- 4. Main Contents and Results
- (1) Introduction of SW Convergence R&D Classification Model Prediction Results and Steps
- Two text mining techniques and three models were experimented to distinguish SW fusion R & D stages. The performance of the model was measured using Accuracy, Precision, and Recall and the results were compared.
- - Accuracy is conducted by combining the correct and correct matching and the middle three steps together to consider one step, and by adjacent matching that is considered correct if actual results and predictions that fall by one step are shown.
-
[Picture 1] Model Specific Accuracy Experiment Results
- (2) Text mining results
- The results of vectoring for text-type inputs used in this study show that tf-idf is on average more predictable than doc2vec, as shown in Table 1
- - Because doc2vec algorithms generally perform better in cases where learning data is high, tf-idf is considered to be a relatively preferable algorithm in current experiments where learning data are relatively small.
- The disadvantage of doc2vec is that in the course of the experiment, the time required to vector the input data as a whole is significantly greater than tf-idf. - [Table 1] Comparison of tf-idf/doc2vec (5 Stage & Linear SVM)
[Table 1] Comparison of tf-idf/doc2vec (5 Stage & Linear SVM) Algorithm Scale Precision Recall f1-
scoretf-idf High 0.59 0.76 0.67 Med High 0.17 0.06 0.09 Medium 0.18 0.07 0.09 Med Low 0.22 0.06 0.09 Low 0.83 0.95 0.89 Accuracy Accurate matches:72.78%
Combined matches:75.31%
Adjacent matches:84.50%doc2vec High 0.57 0.75 0.64 Med High 0.21 0.09 0.12 Medium 0.10 0.05 0.07 Med Low 0.07 0.01 0.03 Low 0.82 0.94 0.88 Accuracy Accurate matches:70.11%
Combined matches:73.19%
Adjacent matches:82.57% - (3) 2017 R&D Project Prediction Results
- 1) Comparing the results of the Linear SVM Model
- Experimental results for the linear SVM model and the tf-idf / doc2vec algorithm showed that the two-stage predicted value of the tf-idf method was most similar to the training data.
- The doc2vec method produces a relatively stable model with a relatively small skew of each stage, with a 2.75% difference in the ratio of the low stage between stages 5 and 2. (tf-idf shows a 5.76 percent difference)
- [Table 2] Classification result summary of 2017 National R&D projects(Linear SVM)
[Table 2] Classification result summary of 2017 National R&D projects(Linear SVM) Stage 5 Stage 3 Stage 2 tf-idf High 4,012 7.22% High 3,022 5.44% High 9,325 16.78% Med High 587 1.06% Medium 4,623 8.32% Low 46,241 83.22% Medium 746 1.34% Low 47,920 86.24% Med Low 776 1.40% Low 49,445 88.98% doc2vec High 3,499 6.30% High 3,005 5.41% High 8,107 14.28% Med High 668 1.20% Medium 4,463 8.03% Low 48,678 85.72% Medium 1,070 1.96% Low 48,098 86.56% Med Low 1,313 2.36% Low 49,017 88.21% -
[Picture 2] Linear SVM & tf-idf’s Stage estimating distribution
- 2) Comparing the results of the Multinomial NB Model
- As shown in Table 3, tf-idf and doc2vec rarely predicted the middle three stages(Med High, Medium, Med Low), and in particular, the Med High stages task was hardly classified.
- In both algorithms, the tasks classified into the low stages in the 5th stage and the 3rd stage show about 90% of the early stages and about 88% of the tasks.
- [Table 3] Classification result summary of 2017 National R&D projects(Multinomial NB)
[Table 3] Classification result summary of 2017 National R&D projects(Multinomial NB) Stage 5 Stage 3 Stage 2 tf-idf High 4,513 7.95% High 2,590 4.56% High 10,477 18.45% Med High 9 0.02% Medium 4,185 7.37% Low 46,308 81.55% Medium 241 0.42% Low 50,010 88.07% Med Low 109 0.19% Low 51,913 91.42% doc2vec High 3,736 6.58% High 2,534 4.46% High 10,129 17.84% Med High 0 0.00% Medium 3,976 7.00% Low 46,656 82.16% Medium 89 0.16% Low 50,275 88.54% Med Low 200 0.35% Low 52,760 92.91% -
[Picture 3] Multinomial NB & tf-idf’s Stage estimating distribution
- (4) Results of expert verification of predictions
- In comparison to the model’s forecast results by performing 100 samples and validating them by SW convergence R&D experts, 86% of the results that SW R&D experts categorize collectively and the results from the automatic classification models
- - The high level matches the two results by 75% and the Med High and Medium levels by 16.7%. Because of the nature of the learning data, the Med High, Medium, and Medium Low levels can be determined that experts and classification models do not match.
- The classification model in this study tends to under-predict the tasks in the middle (med*) phase and is more specialized in the distinction between high and low levels.
- [Table 4] Accurate/Adjacent Match, Non-Matching’s Number and Percentage
[Table 4] Accurate/Adjacent Match, Non-Matching’s Number and Percentage Expert Prediction Count Accurate Matching Adjacent Matching Non-Matching Count Percent Count Percent Count Percent High 8 6 75.0% 0 0.0% 2 25.0% Med High 6 1 16.7% 1 16.7% 4 66.7% Medium 6 1 16.7% 0 0.0% 5 83.3% Med Low 2 0 0.0% 2 100.0% 0 0.0% Low 78 78 100.0% 0 0.0% 0 0.0% 합계 100 86 86.0% 3 3.0% 11 11.0% - (5) Description of model prediction
- This study seeks to provide a basis explanation for classification in order to improve utilization and reliability of classification models, and uses the Lime algorithm to explain the basis for classification of tasks.
- - [Figure 2] describes the basis for classification of data classified in the high phase, which is determined at the high level because "learning" and "big" have a positive effect and "air" and "dest" have a negative effect.
- [Figure 4] Weighted graph of each word for high step judgment

- (6) Analysis and Implication of SW Convergence R&D by Type
- A total of 55,566 prediction results from the 2017 national R&D project will be analyzed for each of the four types.
- ① Performing ministries
- (Status) The most frequently conducted SW convergence R&D based on the five-stage classification and total research costs were the Ministry of Science, Technology, Information and Communication (the Ministry of Science and Technology), the Ministry of Trade, Industry and Energy (the Ministry of Industry and Energy), and the Ministry of Small and Medium-sized Venture Enterprises (the division). And based on the number of assignments, they were surveyed in the order of the Ministry of Science and Technology, the Ministry of Education, and the Mid-term Department.
- - The Ministry of Science and Technology is the most active person in performing the high level tasks, which include more than 80% of SW convergence R&D activities, compared to other ministries
- At the high level, the ministry conducted about 1.8 times more tasks than the Education Ministry (2th) based on the number of tasks, and in terms of total research costs, it accounted for about three times larger than the Ministry of Industry and Energy (2th).
- - The Small and Medium Business Venture Department is the department that carries out the most tasks with 20 to 60% SW convergence R&D activities based on the number of tasks.
- The Ministry of Trade, Industry and Energy (MOTIE) has found that SW convergence R&D activities are most actively carrying out tasks between 40 and 80% (Med High and Medium levels) based on total research costs. - (Implication) Since SW convergence is relatively not carried out in a balanced manner compared to national R&D projects*, strategies for revitalizing SW convergence are needed.
- - The combined portion of the Ministry of Science, ICT and Medium Business accounts for 82.58 percent of the total research costs, while 20 other ministries and agencies are very under 10 percent.
The above three ministries account for 76.38 percent of the total research costs for the entire national R&D project.
- Given that SW convergence has not been balanced by different ministries in national R&D projects, policies such as planning for SW R&D by each ministry to enhance SW convergence and planning and support for SW convergence projects at the pan-ministerial level are required*.
Various statistics such as the Ministry of Health and Welfare, the Ministry of Agriculture, Food and Rural Affairs, and the Korea Meteorological Administration's weather forecast models include the pilot application and expansion of R&D incorporating SW. - ② By Project performer
- (Status) The main subjects of SW convergence are small and medium-sized businesses, government-funded research institute, and universities. However, large companies, mid-sized companies and government-funded research institute showed that their portion of SW convergence projects was very low at less than 5 percent.
- - Small and medium-sized enterprises are the ones that perform the most tasks in all SW convergence R&D phases, except for the low level, based on the basis of total research costs. And universities were found to be the ones who performed the SW convergence R&D tasks most frequently in the high and medium high stages by task count standards.
- The government-funded research institute conducted about 30 percent of all national R&D tasks based on total research costs, but it was found that it was not the main body that actively carried out SW convergence R&D tasks. - (Implication) The proportion of total research costs on national R&D tasks is investigated in reverse order by the government-funded research institute, universities, and small and medium enterprises, and SW convergence tasks in order to promote SW convergence of the participating institutes.
- - Efforts should be made to revitalize SW convergence at government-funded research institute that use more than 30 percent of research funds for national R&D projects. In addition, institutional support should be strengthened to link the research achievements of the government-funded research institute to commercialization through small and medium-sized enterprises, a key player in the SW convergence project.
- ③ Research and development stage
- (Status) The proportion of the total research cost of the national R&D project was high in the order of development, basic and applied research, and SW convergence R&D was the same.
- - SW Convergence R&D is believed to be a phenomenon consistent with SW R&D characteristics, with development research accounting for 52% or more, which is somewhat higher than national R&D.
- (Implication) It seems that SW R&D has characteristics that aim to create products and services rather than to discover new facts that fall into the basic stage.
- ④ National S&T(Science and Technology) Standard Classification System
- (Status) While some areas such as information/communications and electricity/electronics have high SW convergence rates, the degree of SW convergence in life sciences and agriculture is found to be insufficient, which necessitates the establishment of policies for balanced convergence.
- - The information/communication sector is the biggest difference, with 36.7 percent, or more than three times higher than the 11.1 percent share in national R&D projects, in total research costs for SW convergence R&D projects.
- Electricity/electronics, construction/ transportation, culture/art/sports are also found to have a higher ratio of SW convergence R&D compared to the ratio of each field in national R&D projects.
- The fields of life science and agriculture, fisheries, materials and chemical engineering show a significant drop in SW convergence compared to the total research costs of national research and development. - (Implication) There is a difference in level of SW convergence between different fields, which calls for the establishment of strategic portfolios to strengthen global competitiveness in each sector
- - It is necessary to establish strategies for promoting SW convergence by planning tasks through SW convergence R&D and promoting related achievements in life science, agriculture, fisheries, materials and chemical engineering.
- 5. Policy use
- The SW convergence R&D automatic classification model, which is the result of this study, enables analysis of SW convergence status for the entire national R&D project. In addition, data-based trending analysis can be performed annually, saving resources and time spent compared to traditional methods of analysis using experts.
- - Through this process, specific SW convergence R&D status and evidence data can be secured and used as basic data for the establishment of mid- to long-term SW convergence R&D strategies and policies in the future.
- In this study, the criteria for SW convergence R&D determination were established in a quantitative manner rather than a conventional qualitative method, and the research was conducted based on task information provided by NTIS in 2017 to derive the status and issues. It also presented a policy improvement direction for the future activation of SW convergence R&D. - 6. Research Implication and Expected Effects
- This research provided a stepping stone for SW convergence R&D analysis to continuously identify SW convergence phenomena taking place across national R&D projects and compare and analyze trends.
- - Using artificial intelligence technology, we can quickly and accurately compare and analyze the spread of SW convergence on national R&D projects every year by overcoming limitations in existing research that estimate the overall challenges through sampling.
- In addition, text data related to national R&D projects carried out by foreign research institutes such as NSF, DARPA, and EU Horizon 2020 can be obtained to apply an automatic classification model, and the implications can be derived from further studies comparing the results with the domestic situation.
-
-
- 1 2018년의 선행 연구 결과, 과제수 기준으로 15.9%, 총 연구비 기준으로 16.3%가 SW 융합 R&D 과제 인 것으로 조사됨(국가연구개발사업에서의 SW융합에 관한 연구, SPRi, 2018)
-
-
- 제1장 서론
- 제1절 연구의 배경 및 목적
- 1. 연구의 배경
- 2. 연구의 목적
- 3. 연구의 구성
- 제2장 선행 연구 분석
- 제1절 SW 융합 R&D 관련 분석 연구
- 제2절 국가별 SW 융합 기술 발전 정책 및 특징
- 1. 개요
- 2. 미국의 SW 융합 (인공지능) R&D 정책
- 3. 독일의 SW 융합 (인공지능) R&D 정책
- 4. 중국의 SW 융합 (인공지능) R&D 정책
- 5. 일본의 SW 융합 (인공지능) R&D 정책
- 6. 주요국의 SW 융합 (인공지능) R&D 정책 특징 정리
- 제3절 설명 가능한 인공지능(eXplainable AI, XAI)
- 1. 설명 가능한 인공지능의 개념
- 2. LIME(Local Interpretable Model-agnostic Explanations) 알고리즘 개요
- 제3장 연구 프레임워크
- 제1절 연구 자료
- 1. 개요
- 2. 학습데이터의 분포 및 비중 분석
- 제2절 연구 진행 방법
- 1. 개요
- 2. 기계학습을 활용한 분류 모델 개발
- 제4장 기계학습 모델 검증 결과
- 제1절 모델 예측 및 모델별 결과 단계
- 제2절 텍스트 마이닝 결과
- 제3절 분류 모델의 예측 결과 비교 (비중 조정)
- 제5장 SW 융합 R&D 예측 및 검증
- 제1절 2017년 국가연구개발과제의 예측
- 제2절 예측에 대한 전문가 검증
- 제3절 모델 예측에 대한 설명
- 제6장 SW 융합 R&D의 유형별 분석 및 시사점
- 제1절 개요
- 제2절 주요 유형별 분석 내용
- 1. 수행 부처별
- 2. 연구개발 주체별
- 3. 연구개발(R&D) 단계
- 4. 과학기술표준분류체계 (대분류 기준)
- 제3절 SW 융합 현상에 따른 시사점
- 1. SW 융합 현상 분석에 대한 시사점
- 2. SW 융합 현상 분석에 대한 정책적 함의
- 제4절 SW 융합 R&D 정책 방향 제시
- 1. 개요
- 2. 주요 산업 분야에서의 SW 현황
- 3. 한국의 SW 융합 및 AI 정책 현황
- 제5절 연구 의의 및 한계, 향후 방향
- 1. 연구의 의의
- 2. 연구의 한계
- 3. 향후 연구 방향


